Generation Of Computer
Advancement of current computer is ordinarily considered as far as Generation of Computers.There are absolutely five computer generations known till now. Every generation is been talked about here.
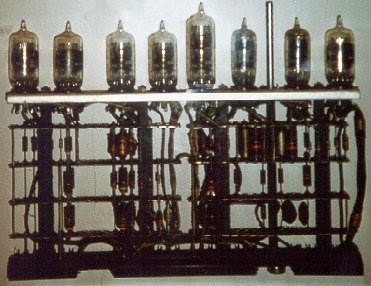
The First Generation
Vacuum Tube: 1940-1956The computers of this generation were made up of vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory. This made computers bulky and heavy. Punched cards were used to feed the information. Magnetic tapes were used as external storage devices. They were very expensive to operate and in addition to using a great deal of electricity, generated a lot of heat and occupied a large amount of space. These machines used machine and assembly level language. The UNIVAC and ENIAC computers are examples of first-generation computing devices.
The Second Generation
Transistors: 1956-1963The computers of this generation made up of transistors replacing vacuum tubes. These were small in size so the machines occupied a less amount of space. The use transistors made the computers work much faster. The transistor was far superior to the vacuum tube, allowing computers to become smaller, faster, cheaper, more energy-efficient and more reliable than their first generation predecessors.
Read: History Of Computers
Though the transistor still generated a great deal of heat that subjected the computer to damage, it was a vast improvement over the vacuum tube. Second generation computers still relied on punched cards for input and printouts for output. The development of higher-level languages like FORTRAN, COBOL and BASIC was possible.
The Third Generation
Integrated Circuits: 1965-1971The computers of these generations were made up of IC (Integrated Circuits). Integrated circuits mean incorporation of hundreds of transistors on a single silicon chip. These were still smaller than the computers of second-generation machines. Heat generated was also less and they occupied less space.
Also Read: Classification Of Computers
Instead of punched cards and printouts, users interacted with third generation computers through keyboards and monitors and interfaced with an operating system, which allowed the device to run many different applications at one time with a central program that monitored the memory. Computers for the first time became accessible to a mass audience because they were smaller and cheaper than their predecessors.
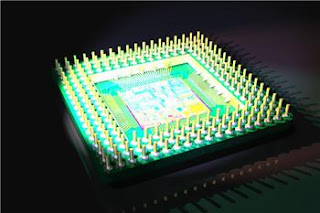
The Fourth Generation
Microprocessors: 1971-PresentFourth Generation computers are the modern day computers. The size started to go down with the improvement in the integrated circuits. Very Large Scale (VLSI) and Ultra Large scale (ULSI) ensured that millions of components could be fit into a small chip. It reduced the size and price of the computers at the same time increasing power, efficiency and reliability. "The Intel 4004 chip, developed in 1971, took the integrated circuit one step further by locating all the components of a computer (central processing unit, memory, and input and output controls) on a minuscule chip."
Due to the reduction of cost and the availability of the computers power at a small place allowed everyday user to benefit. First came the minicomputers, which offered users different applications, the most famous of these, the word processors and spreadsheets, which could be used by non-technical users.
Video game systems like Atari 2600 generated the interest of general populace in the computers.
In 1981, IBM introduced personal computers for home and office use. "The number of personal computers in use more than doubled from 2 million in 1981 to 5.5 million in 1982. Ten years later, 65 million PCs were being used." Computer size kept on getting reduced during the years. It went down from Desktop to Laptops to Palmtops. Macintosh introduced Graphic User Interface in which the users didn’t have to type instructions but could use Mouse for the purpose.
The continued improvement allowed the networking of computers for the sharing of data. Local Area Networks (LAN) and Wide Area Network (WAN), were potential benefits, in that they could be implemented in corporations and everybody could share data over it. Soon, the internet and World Wide Web appeared on the computer scene and fermented the Hi-Tech revolution of 90's.
The Fifth Generation
Artificial Intelligence: Present and BeyondThis is an anticipated new type of computer based on emerging microelectronic technologies with high computing speeds and parallel processing. The development of Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) technology, which can put many more circuits onto an integrated circuit (chip) than is currently possible, and developments in computer hardware and software design may produce computers far more powerful than those in current use.
It has been predicted that such a computer will be able to communicate in natural spoken language with its user; store vast knowledge databases; search rapidly through these databases, making intelligent inferences and drawing logical conclusions; and process images and ‘see’ objects in the way that humans do.
In 1981, Japan's Ministry of International Trade and Industry launched a ten-year project to build the first fifth Generation computer, the ‘parallel inference machine’, consisting of over a thousand microprocessors operating in parallel with each other. By 1992, however, the project was behind schedule and had only produced 256-processor modules. It has since been suggested that research into other technologies, such as neural networks, may present more promising approaches to artificial intelligence, compared to earlier computer generations.
Recommend To Read: Computer Structure - Input Unit




















No comments: